Most performance advice online pushes systems to the edge. Overclocking, aggressive tweaks, registry hacks, and “boost” utilities promise speed but often end in crashes, instability, or premature hardware failure.
At Mindcore Technologies, we take the opposite approach. In business environments, speed only matters if it is stable, sustainable, and safe. A fast system that overheats or crashes during critical work is worse than a slower but reliable one.
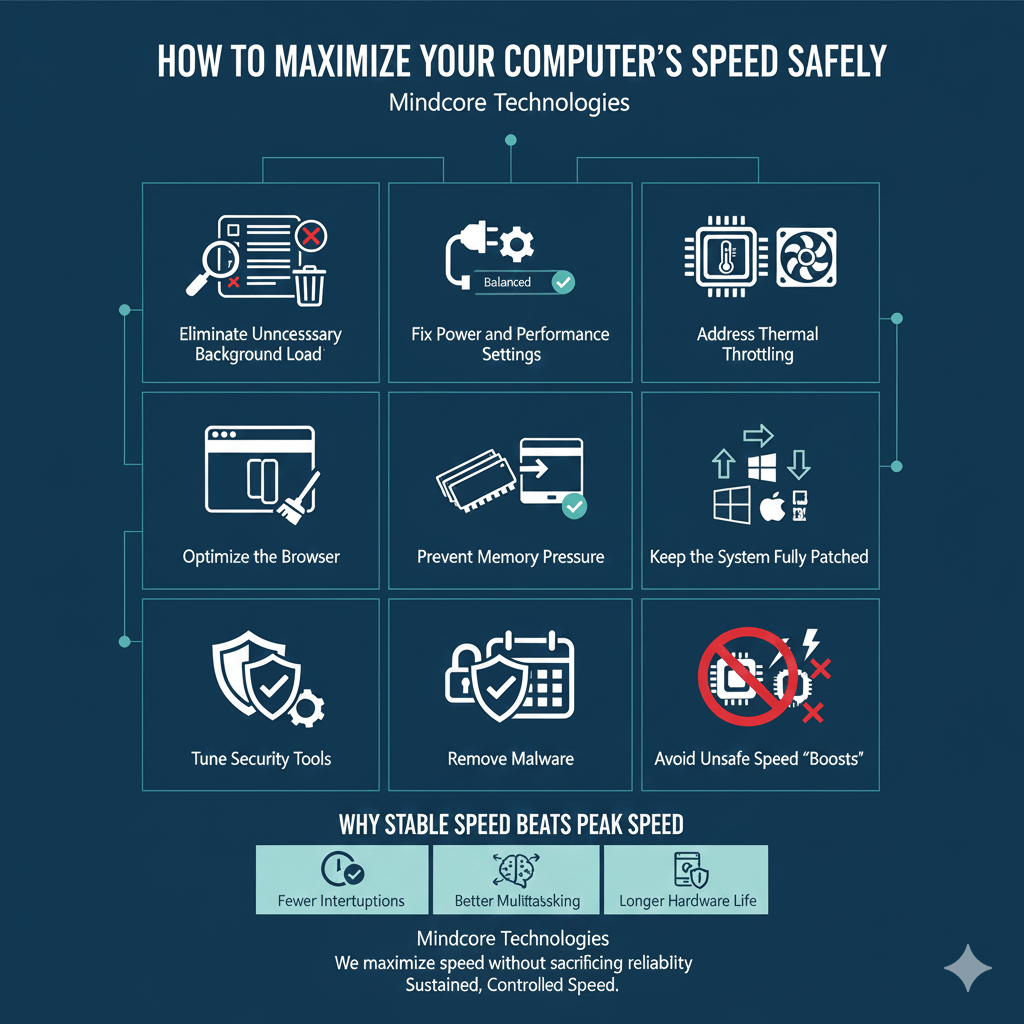
This guide explains how IT professionals maximize computer speed without overheating or crashing, using methods that protect hardware, security, and productivity.
The Core Principle: Remove Friction, Don’t Force Performance
Overheating and crashes occur when systems are pushed beyond what their configuration, cooling, or workload balance can support.
Safe performance gains come from:
- Reducing unnecessary load
- Preventing throttling
- Improving efficiency
- Maintaining thermal stability
We do not force speed. We reclaim it.
1. Eliminate Unnecessary Background Load First
Background processes quietly consume CPU, memory, and disk, increasing heat and instability.
Common culprits:
- Auto-starting applications
- Cloud sync loops
- Vendor utilities
- Legacy services no longer needed
What IT does:
- Audit startup and background processes
- Disable non-essential services
- Remove unused software
Reducing background load lowers heat while improving responsiveness.
2. Fix Power and Performance Settings Correctly
Many systems overheat because they oscillate between power-saving and burst modes.
Problems include:
- Aggressive CPU boosting
- Inconsistent throttling
- Poor performance under sustained load
Safe optimization steps:
- Use Balanced or Performance power modes
- Avoid forcing maximum CPU states permanently
- Verify behavior while plugged in
Proper power tuning improves speed and thermal control.
3. Address Thermal Throttling Before Chasing Speed
Thermal throttling silently kills performance.
Causes:
- Dust buildup
- Poor airflow
- Thin chassis designs
- Degraded thermal materials
IT checks:
- CPU and GPU temperatures under load
- Fan performance
- System logs for thermal events
A cooler system is a faster and more stable system.
4. Optimize the Browser, the Biggest Heat Generator
Browsers drive CPU usage more than most applications.
Common problems:
- Dozens of active tabs
- Persistent web apps
- Poorly written extensions
Safe fixes:
- Remove unnecessary extensions
- Limit always-on tabs
- Reset unstable browser profiles
- Standardize approved browsers
Reducing browser load dramatically lowers CPU temperature and crash risk.
5. Prevent Memory Pressure That Triggers Disk Thrashing
When RAM runs low, systems thrash the disk, generating heat and lag.
Warning signs:
- High CPU and disk usage together
- Freezing during multitasking
IT response:
- Close memory-heavy background apps
- Reduce simultaneous workloads
- Evaluate RAM capacity
CPU efficiency improves when memory is sufficient.
6. Keep the System Fully Patched and Stable
Outdated systems waste resources and behave unpredictably.
Issues include:
- Inefficient scheduling
- Driver conflicts
- Power management bugs
Safe optimization:
- Apply OS updates
- Update chipset, graphics, and thermal drivers
- Remove unsupported software
Stability is a prerequisite for speed.
7. Tune Security Tools Without Creating Heat Spikes
Security software runs constantly and can overheat systems if misconfigured.
Problems we see:
- Overlapping security agents
- Continuous scanning during work hours
- Poor exclusions
Professional approach:
- Eliminate redundant tools
- Tune scan schedules
- Apply vendor-recommended exclusions
Security and performance must be balanced, not traded.
8. Remove Malware That Drives CPU and Heat
Malware often causes unexplained heat and crashes.
Modern threats:
- Run persistently
- Consume CPU quietly
- Trigger instability
Safe response:
- Use enterprise-grade endpoint detection
- Investigate abnormal CPU usage
- Remove persistence mechanisms
Removing malware often resolves both heat and performance issues.
9. Avoid Unsafe Speed “Boosts”
What IT avoids entirely:
- Overclocking business systems
- Registry hacks claiming performance gains
- Third-party “speed booster” software
- BIOS voltage manipulation
These methods increase heat, shorten hardware lifespan, and destabilize systems.
10. Monitor Performance Over Time
Safe optimization is not a one-time action.
IT monitors:
- CPU utilization trends
- Temperature patterns
- Crash logs
- Throttling behavior
- Impact of updates and security tools
Monitoring ensures speed gains persist without side effects.
Why Stable Speed Beats Peak Speed
Peak performance that:
- Overheats
- Crashes
- Throttles unpredictably
Is not usable performance.
Sustained, controlled speed delivers:
- Fewer interruptions
- Better multitasking
- Longer hardware life
- Predictable productivity
This is the standard IT works toward.
How Mindcore Technologies Maximizes Speed Safely
Mindcore helps businesses achieve stable performance through:
- Endpoint performance monitoring
- Background load optimization
- Thermal and power management
- Browser and application tuning
- Security configuration optimization
- Patch and driver management
- Malware and infostealer removal
We maximize speed without sacrificing reliability.
Final Takeaway
Maximizing computer speed safely is not about pushing hardware harder. It is about removing inefficiencies that cause heat, instability, and crashes.
When background load is reduced, power settings are correct, systems are patched, security is tuned, and thermal limits are respected, computers become faster, cooler, and more reliable.