Overview of Networking Needs
One of the very basics that you need to know when you enter networking is how devices communicate over a network. It has an essential role to play in setting up personal networks from complex organizational networks and ensuring that data is routed between devices. Therefore, most networking basically routes data between devices and enables devices to establish communication. A device relies on a great important tool called a subnet mask to communicate with the other devices. But what exactly is a subnet mask and how crucial is it when paired with a zero trust secure workspace platform like ShieldHQ to control and monitor segmented network environments?
Let’s put this concept down in a simple manner so that you will be clear about it and apply it to your networking adventure.
What is a Subnet Mask?
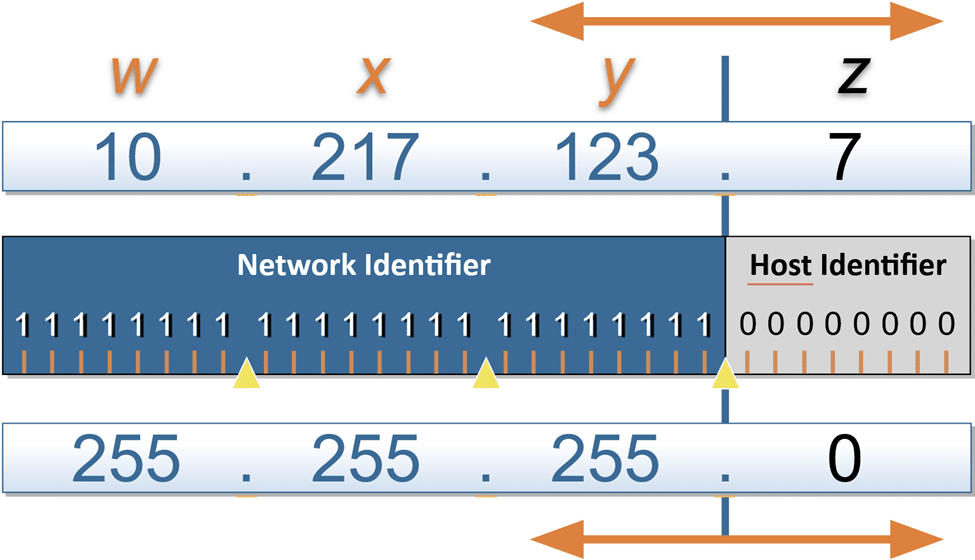
The subnet mask may be generally defined as the 32 bits through which IP addresses are divided into two parts:
- The Network Portion: Identifies the specific network.
- The Host Portion: Identifies individual devices (or “hosts”) within that network.
Think of it as a postal address system. The city name represents the network, and the house number within that city represents the specific device.
Example: 192.168.1.10 – subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
- 192.168.1 is the Network Portion.
- The Host Portion is 10.
This basically tells us that the device belongs to the network 192.168.1, and it is the 10th device in that particular group.
Why To Use Subnet Masks?
One of the factors for managing and organizing networks is great subnet masks. Here’s why:
1. Efficient IP Address Management
Every device on a network requires a unique IP address, and the subnet mask allows the division of a large pool of addresses into smaller sets or subnets. This segmentation helps allocate addresses more effectively, preventing waste.
An example could be that a company dedicates one subnet for its HR, one for its IT, and another for Sales. Each department gets only the IP addresses it needs.
2. Improved Security
Segmentation creates restricted access to sensitive data within a network. Consider hosting the Finance department on its private subnet; by this measure, other undesired users from different departments find it impossible to reach financial records.
3. Better Network Performance
Subnetting minimizes unnecessary network traffic. Devices of one subnet will not send messages to devices of the other subnetwork, with an assurance of decreased congestion thus enriching the performance.
4. Easier Troubleshooting
In the case of a connectivity issue, the problematic section can be isolated by subnetting for network administrators. Hence, diagnosis and repair become quicker and easier.
How Subnet Masks Work
Subnet masks can be generally written in the following two formats:
- Dotted-Decimal Notation: For example, 255.255.255.0.
- CIDR Notation: for instance, /24 (meaning, 24 bits belong to the defined network part).
Dotted Decimal Notation Explained
Every octet in a subnet mask can be treated as an eight-bit binary digit, and the fact determines which part of the IP address is used to identify networks.
- 255.255.255.0: The first three octets “255” refer to the network, while the last octet (0) is for the host.
- 255.255.0.0: The first two octets are for the network, allowing more devices in the host portion.
Simplified CIDR Notation
Classless Inter-Domain Routing or CIDR is an abbreviation referring to subnet masks. A good example of it is /24 which states that the first 24 bits of the IP address are designated for the network: hence, it is equivalent to dotted decimal – 255.255.255.0.
Calculating Subnet Mask
Subnet mask calculation deals with how many devices one will have in a given subnet.
Steps to Calculate:
- Determine the Network Size
How many devices (hosts) will be in this subnet? - Apply the Formula
Use the formula:
Number of Hosts = 2 ( 32 − Network Bits ) − 2
The subtraction of 2 accounts for the network and broadcast addresses.
Example
Let’s say you need a subnet for 50 devices:
- The smallest power of 2 greater than 50 is 64, requiring 6 bits for hosts.
- That leaves 32 – 6 = 26 bits for the network, so the subnet mask is /26 or 255.255.255.192.
- This subnet supports up to 62 hosts, which covers your requirement of 50.
Common Subnet Masks and Their Uses
Here’s a quick reference for some common subnet masks:
| Subnet Mask | CIDR Notation | Hosts per Subnet |
| 255.255.255.0 | /24 | 254 |
| 255.255.255.128 | /25 | 126 |
| 255.255.255.192 | /26 | 62 |
| 255.255.0.0 | /16 | 65,534 |
Select the mask that best fits the number of devices and level of segmentation you need.
Benefits of Subnetting
Subnetting offers a range of benefits for any network:
- Scalability: Accommodates growing networks by allowing new subnets to be added without disrupting existing ones.
- Security: Keeps sensitive data confined to specific subnets.
- Efficiency: Reduces traffic and makes IP address management easier.
Conclusion
It is a fundamental requirement for any network-related job to understand subnet masks. These masks define the network structure, thus contributing to effective communication and security, as well as reduced troubleshooting time.
For a home user just learning to configure a network or an IT person configuring the environment of a multinational corporation, depth in subnet masking gives power to create and maintain solid networks.
CTA: Ready to Take Your Networking Skills to the Next Level? Join Us in Building Smarter Networks.
Dive deeper into the world of subnetting, CIDR notation, and network design principles to unlock the full potential of your network setup. Whether you’re optimizing a home network or managing an enterprise-level system, understanding subnet masks is just the beginning.
Have questions or need help with subnetting? Drop a comment below or reach out to us!